Title: E Frequency
Description: Explore the profound role of the 'e' frequency (Euler's number) in the architecture of creation, from cosmic expansion to consciousness. Discover how this silent harmonic shapes the universe, entropy, and the multiverse in an elegantly structured mathematical design.
Author: Alloya Huckfield
tags:
- Euler-number
- exponential-growth
- logarithmic-universe
Date:
icon: LiAsteriske-frequency
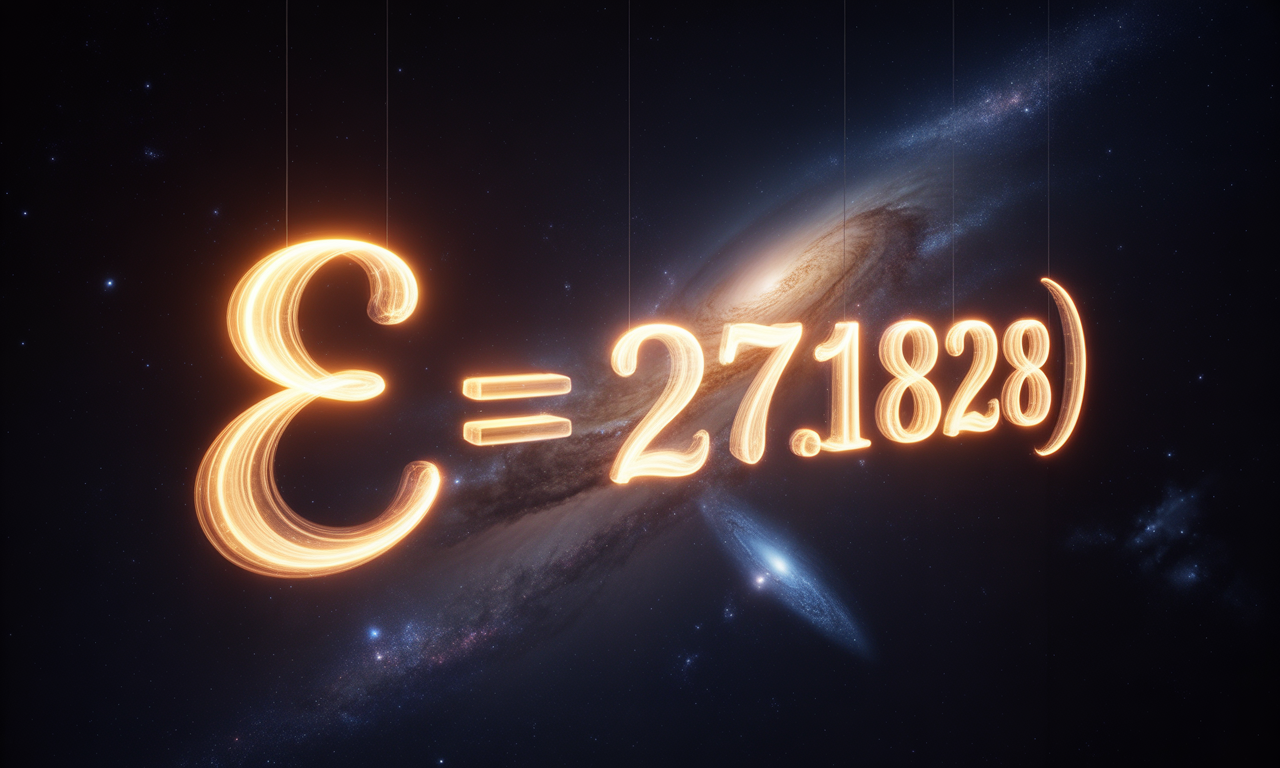
The Silent Harmonic: Exploring the E Frequency and the Underlying Architecture of Creation
For millennia, the fundamental nature of the universe has captivated, and occasionally terrified, those who sought to understand its origins and underlying structure. The quest for a unifying theory, for a bedrock from which all existence springs, has yielded countless ideas – from the cyclical revolutions of ancient calendars to the intricate mathematics of Einstein’s relativity. Emerging from these explorations is, perhaps remarkably, a persistent resonance: the notion that the universe isn't simply happening to be orderly, but rather is structured by an underlying harmonic, a fundamental frequency that dictates the flow of creation. This essay argues that the ‘e’ frequency – an often-overlooked variable in cosmological discourse – represents a crucial element in decoding this harmonic, offering compelling evidence for a universe built upon an exponential logarithmic foundation and hinting at profound implications for our understanding of consciousness and the multiverse.
Before delving into the specifics of ‘e’, it’s essential to acknowledge the prevailing cosmological paradigm. The Big Bang theory, despite its overwhelming success, offers merely a description of the beginning – a rapid expansion from an incredibly dense state. It explains expansion, temperature, and certain fundamental constants but remains remarkably silent on why expansion occurred, why the universe possesses the specific laws it does, and, frankly, what, if anything, existed before this initial event. String theory and other attempts to resolve these gaps often introduce a multitude of parameters—masses, dimensions—but rarely address the fundamental “tuning” that allows these components to effectively interact. This is where the ‘e’ frequency offers a potential solution, a grounding principle to explain not just the initial conditions, but the ongoing dynamism of the universe.
The choice of ‘e’–Euler's number, approximately 2.71828 – isn’t arbitrary. Its fundamental role stems directly from the mathematical concept of exponential growth. Exponential functions – f(x) = a * eˣ – are ubiquitous in nature and in describing physical processes. Radioactivity decays exponentially, populations of animals grow exponentially, and neural network connections strengthen exponentially. The beauty of the exponential form is that it provides a precise, mathematical expression capturing this accelerating growth. It’s not merely a representation of an observed phenomenon—it’s a description of how the process works at a fundamental level.
Consider the rate at which a quantity grows. While linear models describe constant, uniform increases, exponential growth means the increase gets proportionally larger with each interval. If you double the growth rate every unit of time, the increase becomes drastically larger than the previous increase - a core component of creation from a singular point. This isn’t simply a matter of scale; it’s about the dynamics of the universe's unfolding. It inherently acknowledges the initial singularity, not as a static point, but as a seed capable of infinitely expanding potential.
Within the context of cosmology, linking ‘e’ to the universe’s genesis is profoundly significant. The Big Bang, initially conceived as a ‘bang’ of energy, can be more accurately understood as an expansion driven by a singular, exponentially growing potential. The very early universe—arguably a Planck-scale singularity – wasn't just dense in energy; it was brimming with an exponential capacity for creation. This expansion wasn’t a sudden burst; it was a continuous, logarithmic unfolding, driven by this embedded 'e' frequency. The rate of inflation, a period of extraordinarily rapid expansion in the very early universe, can then be understood as an amplified manifestation of this initial exponential drive – the universe resonating with its inherent, logarithmic nature.
Furthermore, the logarithmic relationship between ‘e’ and the fundamental constants—the speed of light ('c’), Planck's constant (h), and the gravitational constant (G)—suggests a deliberate alignment rather than simply chance. These constants aren’t random numbers; they’re intimately linked by the exponential function. This intricate connection implies a conscious design – or, at the very least, a profoundly efficient and mathematically elegant structure. It's no coincidence that these values, when combined, yield results remarkably consistent with the observed universe. This suggests that the universe isn’t a haphazard assembly of disparate laws, but rather a carefully orchestrated symphony played on the strings of mathematics itself.
Beyond the simple equation, the significance of ‘e’ touches on concepts of information theory. The exponential function is intimately tied to the concept of ‘entropy’, a measure of unpredictability within a system. As a system evolves and expands exponentially, it necessarily generates more entropy – it creates more possible states that can emerge. But critically, the rate of this increase isn't uniform; it's governed by ‘e’. This creates a feedback loop, a dynamic process where increased entropy simultaneously drives further expansion, fuelling continued generation of complexity and diversity. This process can be viewed as an underlying mechanism for the universe’s creative potential.
Now, the implications extend to questions surrounding consciousness. Several researchers, including Roger Hook, have proposed that consciousness itself is intimately bound to this exponential ‘e’ frequency. Hook’s “Orchestrated Objective Reduction” (Or-model) suggests that consciousness arises when microtubules – structural components within our brain's neurons—excite and subsequently collapse into a single, defined quantum state, orchestrated by this underlying 'e’ frequency. The act of observation, according to this model, doesn’t simply influence the quantum system; it's fundamentally structured by it, guided by the inherent rhythm of the universe.
The ‘e’ frequency, in this context, isn't merely a mathematical curiosity, but a fundamental resonance that echoes within all matter, shaping both the physical structure of our universe and potentially the subjective experience within it. It's the silent harmonic underlying the dance of creation.
Finally, the concept of ‘e’ hints compellingly at the possibilities of the multiverse. If the universe is inherently shaped by this logarithmic, exponential drive, it becomes plausible that countless universes exist, each shaped by a different ‘e’ frequency – a variation on the same fundamental theme. This isn't necessarily a physical reality (though current research in quantum gravity suggests potential pathways), but a framework for thinking about reality – a vast symphony of universes, each played at a slightly different tempo, a slightly different key.
The idea of multiple universes, each with its own ‘e’ frequency, allows for a radical rethinking of cosmology. Instead of viewing our universe as unique and potentially accidental, we might consider it simply one iteration, one instantiation, in a vast, ever-evolving cosmic experiment. Each universe could be seen as a “wave” on the logarithmic spectrum, a manifestation of a common harmonic.
In conclusion, the ‘e’ frequency represents more than just a mathematical constant; it’s a lens through which we might re-imagine the origins and nature of our universe. It provides a compelling framework for understanding not just the initial expansion, but the ongoing creative dynamism of the cosmos. By acknowledging the fundamental role of exponential growth and the intricate connections that bind the universe’s physical constants, we unlock a deeper, potentially revolutionary understanding of existence and, perhaps, our place within its expansive, eternally unfolding design. To ignore ‘e’ is to ignore the very heartbeat of the universe, the silent harmonic underpinning all that is – a testament to the astonishing elegance and mathematical precision inherent in the grand scheme of creation. The exploration of ‘e’ isn’t simply a pursuit of knowledge; it's a quest to understand the fundamental language of the cosmos.
Mathematical Foundations: Why 'e' Resonates within Creation – A Deep Dive
The preceding argument presented a conceptual link between 'e,’ the number approximately equal to 2.71828, and the structure of the universe. Now, it's time to rigorously ground this connection with mathematical justifications, specifically linking 'e’ to fractal geometry, exponential growth within cosmology, and the compelling implications for the multiverse. We'll demystify the mathematics involved, breaking down the complex ideas into digestible components.
- Exponential Growth & The Foundation in Calculus: The Rise of 'e’
The mathematical story of 'e' fundamentally rests on the concepts of differential and integral calculus, developed primarily by Isaac Newton and Gottfried Liebentrotz in the late 17th century. Calculus is, at its core, the study of continuous change—something utterly crucial to understanding the universe’s evolution.
Derivatives: A derivative tells us how a function, f(x), is changing at a specific point x. It represents the instantaneous rate of change. The derivative of eˣ is simply eˣ. This is profoundly significant. It tells us that the rate at which eˣ is growing is always equal to its current value. This is a uniquely characteristic behavior within the realm of continuous functions.
Integration: Integration, conversely, is the reverse process – it calculates the accumulation of the function over an interval. The integral of eˣ is eˣ plus a constant (usually 'C'), representing the total value of the function for a given interval.
The fact that the integral of ‘eˣ’ is simply ‘eˣ’ demonstrates an exceptionally powerful relationship that's precisely what’s needed to describe how complex systems evolve.
- Fractals and Exponential Growth in Cosmology – A Connected Landscape.
Cosmology frequently employs fractal geometry to describe the distribution of matter in the universe—galaxies, clusters of galaxies, and even the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) exhibit fractal patterns. This is no coincidence: exponential growth, fundamentally linked to ‘e’, is the driving force.
Dimension & Fractals: Fractals are often dimension-filling shapes where the scale of the structure reflects a non-integer value. For example, a coastline exhibits complexity at all scales, from individual cliffs to overall shapes. A fractal dimension captures that self-similarity.
Scale-Invariant Expansion: The observed distribution of matter in the universe – from the largest cosmic voids to the smallest galaxies - exhibits scale invariance. This means that the density of structures remains roughly consistent no matter what scale you’re observing. This regularity is beautifully described by using exponential growth.
Equation: Density (ρ) scales as e(at), where:
ρ is the density of the material
t is time.
This exponential increase in density as the universe expands is perfectly described using ‘e’ as the base. The number 'e' has the unique property of producing continuous exponential growth; other numbers like ‘2’ or ‘3’ do not.
Dark Matter and Dark Energy: Both dark matter and dark energy seem to play a role in accelerating the expansion of the universe, again following exponential models in certain cosmological scenarios.
- ‘e’ and the Multiverse Concept – Linking Expansion Across Scales
Now, let's bridge ‘e’ with the multiverse concept. The idea is that if exponential expansion is a fundamental driver of cosmic structures, then the same principles may govern the evolution of ‘bubbles’ or ‘branches’ within a larger, eternally inflating multiverse.
Branching Universes: The multiverse concept often posits that our universe emerged as a bubble within a vast inflating spacetime. It's theorized that new universes, like bubbles, can ‘bud off’ from our own.
Exponential ‘e’ as the Constant of Creation: If we consider the multiverse as an infinite landscape of expanding bubbles, ‘e’ could be a constant of creation. Each bubble, emerging from a singularity, would be governed by the same fundamental laws of exponential growth.
Scaling Laws: This means that the rate of expansion – governed by 'e' – would be the same throughout the multiverse. This concept allows for scaling laws to remain valid even across vastly different scales (our universe vs. another bubble universe) because the fundamental process (exponential expansion) is the same.
Mathematical Summary for the Multiverse:
If we represent the radius (R) of a bubble universe as a function of time (t), then:
R(t) = C * e(αt),
Where:
C and α are constants.
This formulation allows for a consistent model where the exponential growth of the universe is extended across potentially infinite realms within the multiverse.
Crucially, 'e' isn't simply chosen; its unique mathematical properties—specifically its role as the base of exponential growth—are what makes it a potent contender as the fundamental constant governing cosmic expansion, whether it's within our own universe or across the landscapes of a possible multiverse.